Most Important DBMS interview questions and Answers
1. What are advantages of DBMS over traditional file based systems?
Ans: Database management systems were developed to handle the following difficulties of typical file-processing systems supported by conventional operating systems.
1. Data redundancy and inconsistency
2. Difficulty in accessing data
3. Data isolation – multiple files and formats
4. Integrity problems
5. Atomicity of updates
6. Concurrent access by multiple users
7. Security problems
2. What are super, primary, candidate and foreign keys?
Ans: A superkey is a set of attributes of a relation schema upon which all attributes of the schema are functionally dependent. No two rows can have the same value of super key attributes.
A Candidate key is minimal superkey, i.e., no proper subset of Candidate key attributes can be a superkey.
A Primary Key is one of the candidate keys. One of the candidate keys is selected as most important and becomes the primary key. There cannot be more that one primary keys in a table.
Foreign key is a field (or collection of fields) in one table that uniquely identifies a row of another table. See this for an example.
3. What is the difference between primary key and unique constraints?
Ans: Primary key cannot have NULL value, the unique constraints can have NULL values. There is only one primary key in a table, but there can be multiple unique constrains.
4. What is database normalization?
Ans: It is a process of analyzing the given relation schemas based on their functional dependencies and primary keys to achieve the following desirable properties:
1) Minimizing Redundancy
2) Minimizing the Insertion, Deletion, And Update Anomalies
Relation schemas that do not meet the properties are decomposed into smaller relation schemas that could meet desirable properties.
5. What is SQL?
SQL is Structured Query Language designed for inserting and modifying in a relational database system.
6. What are the differences between DDL, DML and DCL in SQL?
Ans: Following are some details of three.
DDL stands for Data Definition Language. SQL queries like CREATE, ALTER, DROP and RENAME come under this.
DML stands for Data Manipulation Language. SQL queries like SELECT, INSERT and UPDATE come under this.
DCL stands for Data Control Language. SQL queries like GRANT and REVOKE come under this.
7. What is the difference between having and where clause?
Ans: HAVING is used to specify a condition for a group or an aggregate function used in select statement. The WHERE clause selects before grouping. The HAVING clause selects rows after grouping. Unlike HAVING clause, the WHERE clause cannot contain aggregate functions.
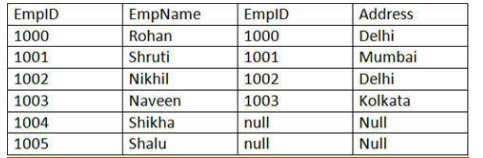
8. What is Join?
Ans: An SQL Join is used to combine data from two or more tables, based on a common field between them. For example, consider the following two tables.
Student Table
ENROLLNO STUDENTNAME ADDRESS
1000 geek1 geeksquiz1
1001 geek2 geeksquiz2
1002 geek3 geeksquiz3
StudentCourse Table
COURSEID ENROLLNO
1 1000
2 1000
3 1000
1 1002
2 1003
Following is join query that shows names of students enrolled in different courseIDs.
SELECT StudentCourse.CourseID, Student.StudentName
FROM StudentCourse
INNER JOIN Customers
ON StudentCourse.EnrollNo = Student.EnrollNo
ORDER BY StudentCourse.CourseID;
The above query would produce following result.
COURSEID STUDENTNAME
1 geek1
1 geek2
2 geek1
2 geek3
3 geek1
9. What is Identity?
Ans: Identity (or AutoNumber) is a column that automatically generates numeric values. A start and increment value can be set, but most DBA leave these at 1. A GUID column also generates numbers; the value of this cannot be controlled. Identity/GUID columns do not need to be indexed.
10. What is a view in SQL? How to create one ?
Ans: A view is a virtual table based on the result-set of an SQL statement. We can create using create view syntax.
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
11. What are the uses of view?
1. Views can represent a subset of the data contained in a table; consequently, a view can limit the degree of exposure of the underlying tables to the outer world: a given user may have permission to query the view, while denied access to the rest of the base table.
2. Views can join and simplify multiple tables into a single virtual table
3. Views can act as aggregated tables, where the database engine aggregates data (sum, average etc.) and presents the calculated results as part of the data
4. Views can hide the complexity of data; for example a view could appear as Sales2000 or Sales2001, transparently partitioning the actual underlying table
5. Views take very little space to store; the database contains only the definition of a view, not a copy of all the data which it presentsv.
6. Depending on the SQL engine used, views can provide extra security
12. What is a Trigger?
Ans: A Trigger is a code that associated with insert, update or delete operations. The code is executed automatically whenever the associated query is executed on a table. Triggers can be useful to maintain integrity in database.
13. What is a stored procedure?
Ans: A stored procedure is like a function that contains a set of operations compiled together. It contains a set of operations that are commonly used in an application to do some common database tasks.
14. What is the difference between Trigger and Stored Procedure?
Ans: Unlike Stored Procedures, Triggers cannot be called directly. They can only be associated with queries.
15. What is a transaction? What are ACID properties?
Ans: A Database Transaction is a set of database operations that must be treated as whole, means either all operations are executed or none of them.
An example can be bank transaction from one account to another account. Either both debit and credit operations must be executed or none of them.
ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) is a set of properties that guarantee that database transactions are processed reliably.
16. What are indexes?
Ans: A database index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and the use of more storage space to maintain the extra copy of data.
Data can be stored only in one order on disk. To support faster access according to different values, faster search like binary search for different values is desired, For this purpose, indexes are created on tables. These indexes need extra space on disk, but they allow faster search according to different frequently searched values.
17. What are clustered and non-clustered Indexes?
Ans: Clustered indexes is the index according to which data is physically stored on disk. Therefore, only one clustered index can be created on a given database table.
Non-clustered indexes don’t define physical ordering of data, but logical ordering. Typically, a tree is created whose leaf point to disk records. B-Tree or B+ tree are used for this purpose.
Other Important Questions
18. What is DBMS?
Ans. Database Management System (DBMS) is a collection of programs that enables user to store, retrieve, update, and delete information from a database.
19. What is RDBMS?
Ans. Relational Database Management system (RDBMS) is a type of DBMS that is based on the relational model. Data from relational database can be accessed or reassembled in many different ways without having to reorganize the database tables.
20. What is a ‘record’ in a database?
Ans. A ‘record’ is the collection of values/fields of a specific entity.
21. What is a ‘field’ in a database?
Ans. A ‘field’ is an area within a record reserved for a specific piece of data.
22. What are database languages? What are the types?
Ans. Database languages are used to write or create database management system. There are three types: data definition language, data manipulation language and query language.
23. Name the various relationships of database. Describe briefly.
Ans.
One-to-one: Single table having drawn relationship with another table having similar kind of columns.
One-to-many: Two tables having primary and foreign key relation.
Many-to-many: Junction table having many tables related to many tables.
24. What is ‘normalization’?
Ans. Organized data void of inconsistent dependency and redundancy within a database is called ‘normalization.
25. What are the different type of normalization?
Ans. The different types of normalization are –
- First Formal Form (1NF),
- Second Normal Form (2NF),
- Third Normal Form (2NF).
26. What is a ‘primary key’?
Ans. A ‘primary key’ is a column whose values uniquely identify every row in a table. Primary key values can never be reused.
27. What is ‘denormalization’?
Ans. Boosting up database performance, adding of redundant data which in turn helps rid of complex data is called ‘denormalization’.
28. What are the conditions to be met for a field to be defined as primary key?
Ans.
- No two rows can have the same primary key value.
- Every row must have a primary key value.
- The primary key field cannot be null.
- Value in a primary key column can never be modified or updated, if any foreign key refers to that primary key.
29. What is a ‘composite key’?
Ans. A ‘composite key’ is a combination of two or more columns in a table that can be used to uniquely identify each row in the table.
30. What is a ‘foreign key’?
Ans. A ‘foreign key’ is a field (or collection of fields) in one table that uniquely identifies a row of another table or the same table.
31. What is a ‘unique key’?
Ans. Unique key is same as primary with the difference being the existence of null. Unique key field allows one value as NULL value.
32. What is a ‘cursor’?
Ans. A database object which helps in manipulating data row by row representing a result set is called cursor.
33. What are the different types of cursors? Define .
Ans.
Dynamic: it reflects changes while scrolling.
Static: doesn’t reflect changes while scrolling and works on recording of snapshot.
Keyset: data modification without reflection of new data is seen.
34. What is a ‘sub-query’?
Ans. A query contained by a query is called sub-query.
35. What is a ‘view’?
Ans. The views are virtual tables. Unlike tables that contain data, views simply contain queries that dynamically retrieve data when used.
36. What is a materialized view?
Ans. Materialized views are also a view but are disk based. Materialized views get updates on specific duration, based upon the interval specified in the query definition. It can be indexed.
37. Define ‘join’ .
Ans. Joins help in explaining the relation between different tables. These are some of the popular questions asked in a Database interview. Always be prepared to answer all types of questions — technical skills, interpersonal, leadership or methodology. If you are someone who has recently started your career in database management, you can enrol in a database certification course to get the techniques and skills required to be an expert in the field.
Slightly Asked Questions :
38. What do you understand by ‘Database’?
Ans: Database is an organized collection of related data where the data is stored and organized to serve some specific purpose.
For Example, A librarian maintains a database of all the information related to the books that are available in the library.
39. Define DBMS.
Ans: DBMS stands for Database Management system. It is a collection of application programs which allow the user to organize, restore and retrieve information about data efficiently and as effectively as possible.
Some of the popular DBMS’s are MySql, Oracle, Sybase, etc.
40. Define RDBMS.
Ans: Relational Database Management System(RDBMS) is based on a relational model of data that is stored in databases in separate tables and they are related to the use of a common column. Data can be accessed easily from the relational database using Structured Query Language (SQL).
41. Enlist the advantages of DBMS.
Ans: The Advantages of DBMS includes:
- Data is stored in a structured way and hence redundancy is controlled.
- Validates the data entered and provide restrictions on unauthorized access to the database.
- Provides backup and recovery of the data when required.
- Provides multiple user interfaces.
42. What do you understand by Data Redundancy?
Ans: Duplication of data in the database is known as Data redundancy. As a result of Data Redundancy, duplicated data is present at various locations, hence it leads to wastage of the storage space and the integrity of the database is destroyed.
43. What are the various types of relationships in Database? Define them.
Ans: There are 3 types of relationships in Database:
One-to-one: One table has the relationship with another table having the similar kind of column. Each primary key relates to only one or no record in the related table.
One-to-many: One table has a relationship with another table that has primary and foreign key relation. The primary key table contains only one record that relates to none, one or many records in the related table.
Many-to-many: Each record in both the tables can relate to many numbers of record in another table.
44. Explain Normalization and De-Normalization.
Ans: Normalization is the process of removing the redundant data from the database by splitting the table in a well-defined manner in order to maintain data integrity. This process saves much of the storage space.
De-normalization is the process of adding up redundant data on the table in order to speed up the complex queries and thus achieve better performance.
45. What are the different types of Normalization?
Ans: Different Types of Normalization are:
- First Normal Form (1NF): A relation is said to be in 1NF only when all the entities of the table contain unique or atomic values.
- Second Normal Form (2NF): A relation is said to be in 2NF only if it is in 1NF and all the non-key attribute of the table is fully dependent on the primary key.
- Third Normal Form (3NF): A relation is said to be in 3NF only if it is in 2NF and every non-key attribute of the table is not transitively dependent on the primary key.
46. What is BCNF?
Ans: BCNF is Boyce Code Normal form. It is the higher version of 3Nf which does not have any multiple overlapping candidate keys.
47. What is SQL?
Ans: Structured Query language, SQL is an ANSI(American National Standard Institute) standard programming language which is designed specifically for storing and managing the data in the relational database management system (RDBMS) using all kinds of data operations.
48. How many SQL statements are used? Define them.
Ans: SQL statements are basically divided into three categories, DDL, DML, and DCL.
They can be defined as:
Data Definition Language (DDL) commands are used to define the structure that holds the data. These commands are auto-committed i.e. changes done by the DDL commands on the database are saved permanently.
Data Manipulation Language (DML) commands are used to manipulate the data of the database. These commands are not auto-committed and can be rolled back.
Data Control Language (DCL) commands are used to control the visibility of the data in the database like revoke access permission for using data in the database .
49. Enlist some commands of DDL, DML, and DCL.
Ans:
Data Definition Language (DDL) commands:
- CREATE to create a new table or database.
- ALTER for alteration.
- Truncate to delete data from the table.
- DROP to drop a table.
- RENAME to rename a table.
Data Manipulation Language (DML) commands:
- INSERT to insert a new row.
- UPDATE to update an existing row.
- DELETE to delete a row.
- MERGE for merging two rows or two tables.
Data Control Language (DCL) commands:
- COMMIT to permanently save.
- ROLLBACK to undo the change.
- SAVEPOINT to save temporarily.
50. Define DML Compiler.
Ans: DML compiler translates DML statements in a query language into a low-level instruction and the generated instruction can be understood by Query Evaluation Engine.
51. What is DDL interpreter?
Ans: DDL Interpreter interprets the DDL statements and records the generated statements in the table containing metadata.
52. Enlist the advantages of SQL.
Ans: Advantages of SQL are:
- Simple SQL queries can be used to retrieve a large amount of data from the database very quickly and efficiently.
- SQL is easy to learn and almost every DBMS supports SQL.
- It is easier to manage the database using SQL as no large amount of coding is required.
53. Explain the terms ‘Record’, ‘Field’ and ‘Table’ in terms of database.
Ans:
Record: Record is a collection of values or fields of a specific entity. Eg. An employee, Salary account, etc.
Field: A field refers to an area within a record which is reserved for a specific piece of data. Eg. Employee ID.
Table: Table is the collection of records of specific types. E.g. Employee table is a collection of record related to all the employees.
54. What do you understand by Data Independence?What are its two types?
Ans: Data Independence refers to the ability to modify the schema definition in one level in such a way that it does not affect the schema definition in the next higher level.
The 2 types of Data Independence are:
- Physical Data Independence: It modifies the schema at the physical level without affecting the schema at the conceptual level.
- Logical Data Independence: It modifies the schema at the conceptual level without affecting or causing changes in the schema at the view level.
55. Define the relationship between ‘View’ and ‘Data Independence’.
Ans: View is a virtual table which does not have its data on its own rather the data is defined from one or more underlying base tables.
Views account for logical data independence as the growth and restructuring of base tables is not reflected in views.
56. What are the advantages and disadvantages of views in the database?
Ans:
Advantages of Views:
- As there is no physical location where the data in views is stored, it generates output without wasting resources.
- Data access is restricted as it does not allow commands like insertion, updation, and deletion.
Disadvantages of Views:
- View becomes irrelevant if we drop a table related to that view.
- More memory is occupied when the view is created for large tables.
57. What do you understand by Functional dependency?
Ans: A relation is said to be in Functional dependency when one attribute uniquely defines another attribute.
For Example, R is a Relation, X and Y are two attributes. T1 and T2 are two tuples. Then,
T1[X]=T2[X] and T1[Y]=T2[Y] means the value of component X uniquely define the value of component Y.
Also, X->Y means Y is functionally dependent on X.
58. When is functional dependency said to be the fully functional dependency?
Ans: To fulfill the criteria of fully functional dependency, the relation must meet the requirement of functional dependency.
A functional dependency ‘A’ and ‘B’ is said to be fully functional dependent when removal of any attribute say ‘X’ from ‘A’ means the dependency does not hold anymore.
59. What do you understand by E-R model?
Ans: E-R model is an Entity-Relationship model which defines the conceptual view of the database.
E-R model basically shows the real world entities and their association/relations. Entities here represent the set of attributes in the database.
60. Define Entity, Entity type, and Entity set.
Ans:
Entity can be anything, be it a place, class or object which has an independent existence in the real world.
Entity type represents a set of entities which have similar attributes.
Entity set in the database represents a collection of entities having a particular entity type.
61. Define Weak Entity set.
Ans: Weak entity set is the one whose primary key comprises of its partial key as well as the primary key of its parent entity.
This is the case because the entity set may not have sufficient attributes to form a primary key.
62. Explain the terms ‘Attribute’ and ‘Relations’
Ans: Attribute describes the properties or characteristics of an entity.
For Example, Employee ID, Employee Name, Age, etc., can be attributes of the entity Employee.
Relation is a two-dimensional table containing a number of rows and columns where every row represents a record of the relation. Here, rows are also known as ‘Tuples’ and columns are known as ‘Attributes’.
63. What are VDL and SDL?
Ans: VDL is View Definition language which represents user views and their mapping to the conceptual schema.
SDL is Storage Definition Language which specifies the mapping between two schemas.
64. Define Cursor and its types.
Ans: Cursor is a temporary work area which stores the data as well as the result set occurred after manipulation of data retrieved. A cursor can hold only one row at a time.
The 2 types of Cursor are:
Implicit cursors are declared automatically when DML statements like INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE is executed.
Explicit cursors have to be declared when SELECT statements which are returning more than one row are executed.
65. What is Database transaction?
Ans: Sequence of operation performed which changes the consistent state of the database to another is known as the database transaction. After the completion of the transaction, either the successful completion is reflected in the system or the transaction fails and no change is reflected.
66. Define Database Lock and its types.
Ans: Database lock basically signifies the transaction about the current status of the data item i.e. whether that data is being used by other transactions or not at the present point of time.
There are two types of Database lock which are Shared Lock and Exclusive Lock.
67. What is Data Warehousing?
Ans: The storage as well as access to data, that is being derived from the transactions and other sources, from a central location in order to perform the analysis is called Data Warehousing.
68. What do you understand by Join?
Ans: Join is the process of explaining the relationship between different tables by combining columns from one or more table having common values in each. When a table joins with itself, it is known as Self Join.
69. What do you understand by Index hunting?
Ans: Index hunting is the process of boosting the collection of indexes which help in improving the query performance as well as the speed of the database.
70. How to improve query performance using Index hunting?
Ans: Index hunting help in improving query performance by:
- Using query optimizer to coordinate queries with the workload.
- Observing the performance and effect of index and query distribution.
71. Differentiate between ‘Cluster’ and ‘Non-cluster’ index.
Ans: Clustered Index alters the table and reorders the way in which the records are stored in the table. Data retrieval is made faster by using the clustered index.
A Non-clustered index does alter the records that are stored in the table but creates a completely different object within the table.
72. What are the disadvantages of a Query?
Ans: Disadvantages of a Query are:
- Indexes are not present.
- Stored procedures are excessively compiled.
- Difficulty in interfacing.
73. What do you understand by Fragmentation?
Ans: Fragmentation is a feature which controls the logical data units, also known as fragments that are stored at different sites of a distributed database system.
74. Define Join types.
Ans: Given below are the types of Join, which are explained with respect to the tables as an Example:
employee table:
employee_info table:
1) Inner JOIN: Inner JOIN is also known as a simple JOIN. This SQL query returns result from both the tables having a common value in rows. SQL Query:
SELECT * from employee, employee_info WHERE employee.EmpID = employee_info.EmpID ;
Result:
2) Natural JOIN: This is a type of Inner JOIN which returns results from both the tables having same data values in the columns of both the tables to be joined.
SQL Query:
SELECT * from employee NATURAL JOIN employee_info;
Result:
3) Cross JOIN: Cross JOIN return results as all the records where each row from the first table is combined with each row of the second table.
SQL Query:
SELECT * from employee CROSS JOIN employee_info;
Result:
Let us do some modification in the above tables to understand Right JOIN, Left JOIN, and Full JOIN.
employee table:
employee_info table:
1) Right JOIN: Right JOIN is also known as Right Outer JOIN. This returns all the rows as a result from the right table even if the JOIN condition does not match any records in the left table.
SQL Query:
SELECT * from employee RIGHT OUTER JOIN employee_info on (employee.EmpID = employee_info.EmpID);
Result:
2) Left JOIN: Left JOIN is also known as Left Outer JOIN. This returns all the rows as a result of the left table even if JOIN condition does not match any records in the right table. This is exactly the opposite of Right JOIN.
SQL Query:
SELECT * from employee LEFT OUTER JOIN employee_info on (employee.EmpID = employee_info.EmpID);
Result:
3) Outer/Full JOIN: Full JOIN return results in combining the result of both the Left JOIN and Right JOIN.
SQL Query:
SELECT * from employee FULL OUTER JOIN employee_info on (employee.EmpID = employee_info.EmpID);
Result:
75. What do you understand by ‘Atomicity’ and ‘Aggregation’?
Ans: Atomicity is the condition where either all the actions of the transaction are performed or none. This means, when there is an incomplete transaction, database management system itself will undo the effects done by the incomplete transaction.
Aggregation is the concept of expressing the relationship with the collection of entities and their relationships.
76. Define Phantom deadlock.
Ans: Phantom deadlock detection is the condition where the deadlock does not actually exist but due to a delay in propagating local information, deadlock detection algorithms identify the deadlocks.
77. Define checkpoint.
Ans: Checkpoint declares a point before which all the logs are stored permanently in the storage disk and is the inconsistent state. In the case of crashes, the amount of work and time is saved as the system can restart from the checkpoint.
78. What is Database partitioning?
Ans: Database partitioning is the process of partitioning tables, indexes into smaller pieces in order to manage and access the data at a finer level. This process of partitioning reduces the cost of storing a large amount of data as well as enhances the performance and manageability.
79. Explain the importance of Database partitioning.
Ans: The importance of Database partitioning are:
- Improves query performance and manageability.
- Simplifies common administration tasks.
- Acts as a key tool for building systems with extremely high availability requirements.
- Allows accessing a large part of a single partition.
80. Explain Data Dictionary.
Ans: Data dictionary is a set of information describing the content and structure of the tables and database objects. The job of the information stored in the data dictionary is to control, manipulate and access the relationship between database elements.
81. Explain Primary Key and Composite Key.
Ans: Primary key is that column of the table whose every row data is uniquely identified. Every row in the table must have a primary key and no two rows can have the same primary key. Primary key value can never be null nor can be modified or updated.
Composite Key is a form of the candidate key where a set of columns will uniquely identify every row in the table.
82. What do you understand by Unique key?
Ans: A Unique key is same as the primary key whose every row data is uniquely identified with a difference of null value i.e. Unique key allows one value as NULL value.
83. What do you understand by Database Triggers?
Ans: A set of commands that automatically get executed when an event like Before Insert, After Insert, On Update, On Delete of row occurs in a table is called as Database trigger.
84. Define Stored procedures.
Ans: A Stored procedure is a collection of pre-compiled SQL Queries, which when executed denotes a program taking input, process and gives the output.
85. What do you understand by B-Trees?
Ans: B-Tree represents the data structure in the form of a tree for external memory that reads and writes large blocks of data. It is commonly used in databases and file systems where all the insertions, deletions, sorting, etc., are done in logarithmic time.
86. Name the different data models that are available for database systems.
Ans: Different data models are:
- Relational model
- Network model
- Hierarchical model
87. Differentiate between ‘DELETE’, ‘TRUNCATE’ and ‘DROP’ commands.
Ans: After the execution of ‘DELETE’ operation, COMMIT and ROLLBACK statements can be performed to retrieve the lost data.
After the execution of ‘TRUNCATE’ operation, COMMIT, and ROLLBACK statements cannot be performed to retrieve the lost data.
‘DROP’ command is used to drop the table or key like the primary key/foreign key.
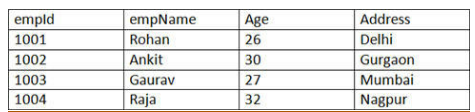
88. Based on the given table, solve the following queries.
Employee table
1) Write the SELECT command to display the details of the employee with empid as 1004.
Ans:
SELECT empId, empName, Age, Address from Employee WHERE empId = 1004;
Result:
2) Write the SELECT command to display all the records of table Employee.
Ans:
SELECT * from Employee;
Result:
3) Write the SELECT command to display all the records of the employee whose name starts with the character ‘R’.
Ans:
SELECT * from Employee WHERE empName LIKE ‘R%’;
Result:
4) Write a SELECT command to display id, age and name of the employees with their age in both ascending and descending order.
Ans:
SELECT empId, empName, Age from Employee ORDER BY Age;
Result:
SELECT empId, empName, Age from Employee ORDER BY Age Desc;
Result:
5) Write the SELECT command to calculate the total amount of salary on each employee from the below Emp table.
Emp table:
Ans:
SELECT empName, SUM(Salary) from Emp GROUP BY empName;
Result: